Inefficiencies of Traditional WAN
Traditional WANs (Wide Area Networks) have several inefficiencies that make them less suitable for modern networking needs, especially with the increasing demand for cloud services, remote work, and high-bandwidth applications. Here are some key inefficiencies of traditional WANs:
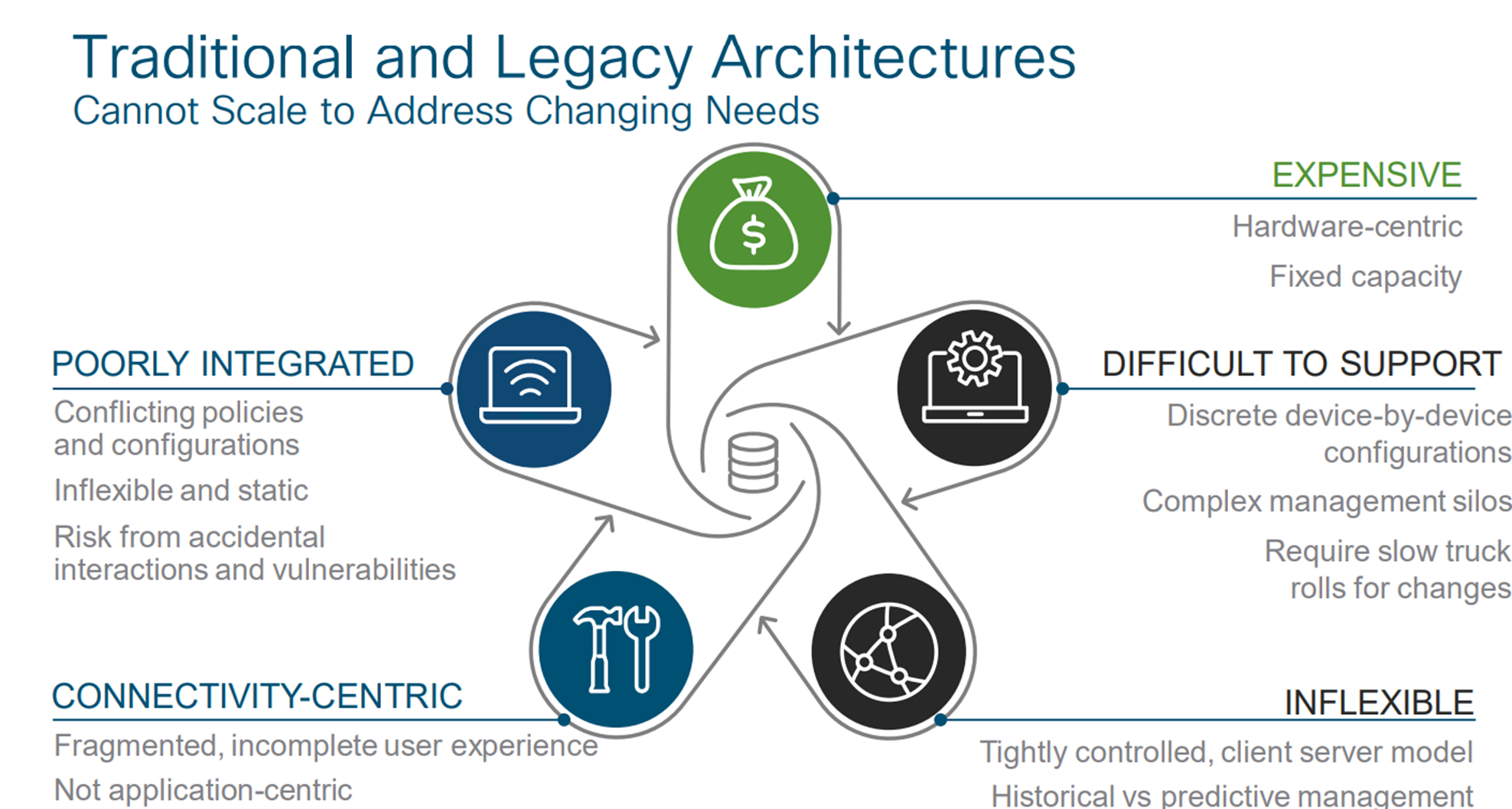
1. High Costs
- Expensive MPLS Circuits: Traditional WANs often rely on MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) circuits, which are costly compared to broadband internet connections.
- Fixed Bandwidth Costs: Organizations must often overprovision bandwidth to accommodate peak usage, leading to higher costs even when the additional capacity is not consistently needed.
2. Complexity and Lack of Agility
- Complex Configuration: Traditional WANs require manual configuration of routers and other networking devices, which is time-consuming and prone to human error.
- Slow Deployment: Setting up new sites or making changes to the network can take weeks or even months due to the manual processes involved.
3. Limited Scalability
- Rigid Architecture: Traditional WAN architectures are not designed to easily scale with the dynamic needs of modern businesses. Adding new locations or increasing bandwidth can be complex and costly.
- Hardware Dependency: Scalability is often limited by the physical hardware used in traditional WANs, making it difficult to quickly adapt to changing business needs.
4. Poor Cloud and SaaS Performance
- Backhauling Traffic: Traditional WANs often route all traffic through a central data center before reaching cloud services, introducing unnecessary latency and reducing application performance.
- Inefficient Cloud Access: With the rise of cloud and SaaS applications, traditional WANs struggle to provide direct and efficient access, leading to poor user experience.
5. Limited Visibility and Control
- Fragmented Management: Traditional WANs lack centralized management, making it difficult to have a unified view of network performance and security across all locations.
- Reactive Troubleshooting: Network issues often require reactive troubleshooting, which can be slow and inefficient without comprehensive visibility and real-time monitoring.
6. Suboptimal Traffic Management
- Static Routing: Traditional WANs typically use static routing, which does not adapt to real-time network conditions. This can lead to suboptimal performance and inefficient use of available bandwidth.
- Lack of Traffic Prioritization: Without advanced traffic management capabilities, traditional WANs cannot prioritize critical applications or optimize traffic flows effectively.
7. Security Challenges
- Perimeter-Based Security: Traditional WANs often rely on perimeter-based security models that are not well-suited to modern, decentralized networks with numerous remote users and cloud-based services.
- Complex Security Management: Implementing and managing security policies across a traditional WAN can be complex and inconsistent, increasing the risk of security breaches.
8. Reliability and Redundancy Issues
- Single Points of Failure: Traditional WANs often have single points of failure, such as relying on a single MPLS circuit for connectivity, which can lead to network outages.
- Limited Redundancy: Implementing redundancy and failover capabilities is more challenging and costly in traditional WAN setups.
Why do we need SD-WAN?
SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) is becoming increasingly important for modern businesses due to several compelling reasons. Here are some of the key benefits and reasons why organizations adopt SD-WAN:
1. Cost Efficiency
- Reduced WAN Costs: Traditional WANs often rely on expensive MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) circuits. SD-WAN allows the use of more cost-effective broadband internet connections alongside or instead of MPLS, reducing overall WAN costs.
- Operational Savings: SD-WAN simplifies network management and reduces the need for specialized network engineering, which can lead to lower operational expenses.
2. Improved Performance
- Optimized Traffic Routing: SD-WAN intelligently routes traffic based on real-time network conditions, ensuring optimal performance for critical applications by avoiding congestion and minimizing latency.
- Enhanced Application Performance: By prioritizing and steering traffic for important applications, SD-WAN helps ensure that mission-critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and low-latency paths.
3. Increased Agility and Flexibility
- Rapid Deployment: SD-WAN allows for quicker deployment of new sites or changes to the network, often in a matter of days rather than weeks or months required by traditional WANs.
- Simplified Configuration: Centralized management and configuration through a software interface make it easier to implement changes and manage policies across multiple locations.
4. Enhanced Security
- Integrated Security: SD-WAN often includes built-in security features such as encryption, firewall capabilities, and intrusion detection/prevention systems. This ensures that data traveling over public internet connections is secure.
- Segmentation: SD-WAN enables network segmentation, allowing organizations to isolate different types of traffic and apply specific security policies to each segment.
5. Improved Visibility and Control
- Centralized Management: SD-WAN provides a centralized management console, offering comprehensive visibility into the network’s performance, traffic patterns, and security status.
- Granular Policy Enforcement: IT teams can create and enforce detailed policies that govern how different types of traffic are handled, ensuring compliance with organizational requirements.
6. Support for Cloud and SaaS
- Cloud Connectivity: SD-WAN is designed to support cloud and SaaS applications, providing direct and optimized access to cloud services without backhauling traffic through a central data center.
- Improved User Experience: By routing traffic directly to the cloud, SD-WAN reduces latency and improves the user experience for cloud-based applications.
7. Scalability
- Easily Scalable: SD-WAN solutions are highly scalable, allowing businesses to expand their network as they grow, without the need for significant additional hardware or complex reconfigurations.
8. Resilience and Reliability
- Redundant Connections: SD-WAN can utilize multiple types of connections (broadband, LTE, MPLS) and dynamically switch between them in case of failure, ensuring high availability and reliability.
- Load Balancing: Traffic can be balanced across multiple connections, improving overall network performance and reliability.
Summary
SD-WAN provides a more flexible, cost-effective, and efficient way to manage wide-area networks, especially for organizations that rely heavily on cloud services, remote work, and multiple branch locations. Its ability to improve performance, security, and manageability while reducing costs makes it an attractive option for modern businesses looking to enhance their network infrastructure.


