Summary of Microsoft Entra ID
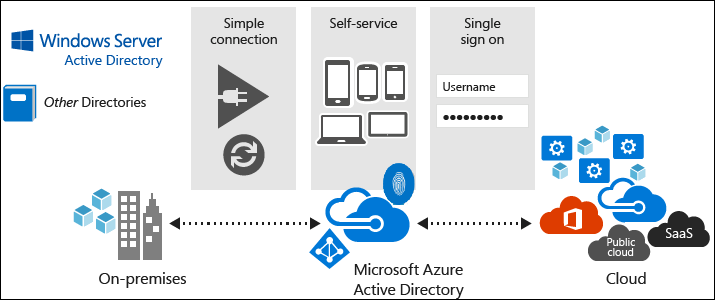
Microsoft Entra ID is a cloud-based identity management service that differs from traditional Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) by focusing on authentication, authorization, and access management for cloud applications. It is a Platform as a Service (PaaS) and doesn’t require users to deploy or manage infrastructure.
Key Features of Microsoft Entra ID:
- Cloud-based identity service with support for multi-factor authentication, identity protection, and self-service password reset.
- Manages user access to cloud applications via Single Sign-On (SSO) and Azure RBAC.
- Allows organizations to extend their on-premises AD DS to the cloud and configure federation for seamless access.
- Provides security features like Conditional Access, Application Proxy, and irregular sign-in detection.
Microsoft Entra Tenants:
- Multi-tenant by design, ensuring isolation between organizations.
- Each Azure subscription must be linked to one Microsoft Entra tenant, but a tenant can support multiple subscriptions.
- Tenants are assigned a default onmicrosoft.com domain but can use custom domains.
Microsoft Entra Schema & Object Management:
- Does not support traditional computer domain membership (e.g., no Group Policy Objects).
- Uses modern management techniques to handle user, device, and application data.
- Applications are represented using Application and servicePrincipal objects, enabling cross-tenant app usage.
Comparison with AD DS:
- AD DS is more focused on on-premises directory services, while Microsoft Entra ID is optimized for cloud-based identity and access management.
- Microsoft Entra ID lacks OUs (Organizational Units) but uses groups for organization and delegation.
Tiers & Licensing:
- The Free tier is included with any Azure subscription.
- Paid tiers (Basic & Premium) offer advanced identity management features, often bundled with Microsoft 365.
Microsoft Entra ID serves as the identity provider for Microsoft 365 and Azure, handling billions of authentication requests weekly. 🚀
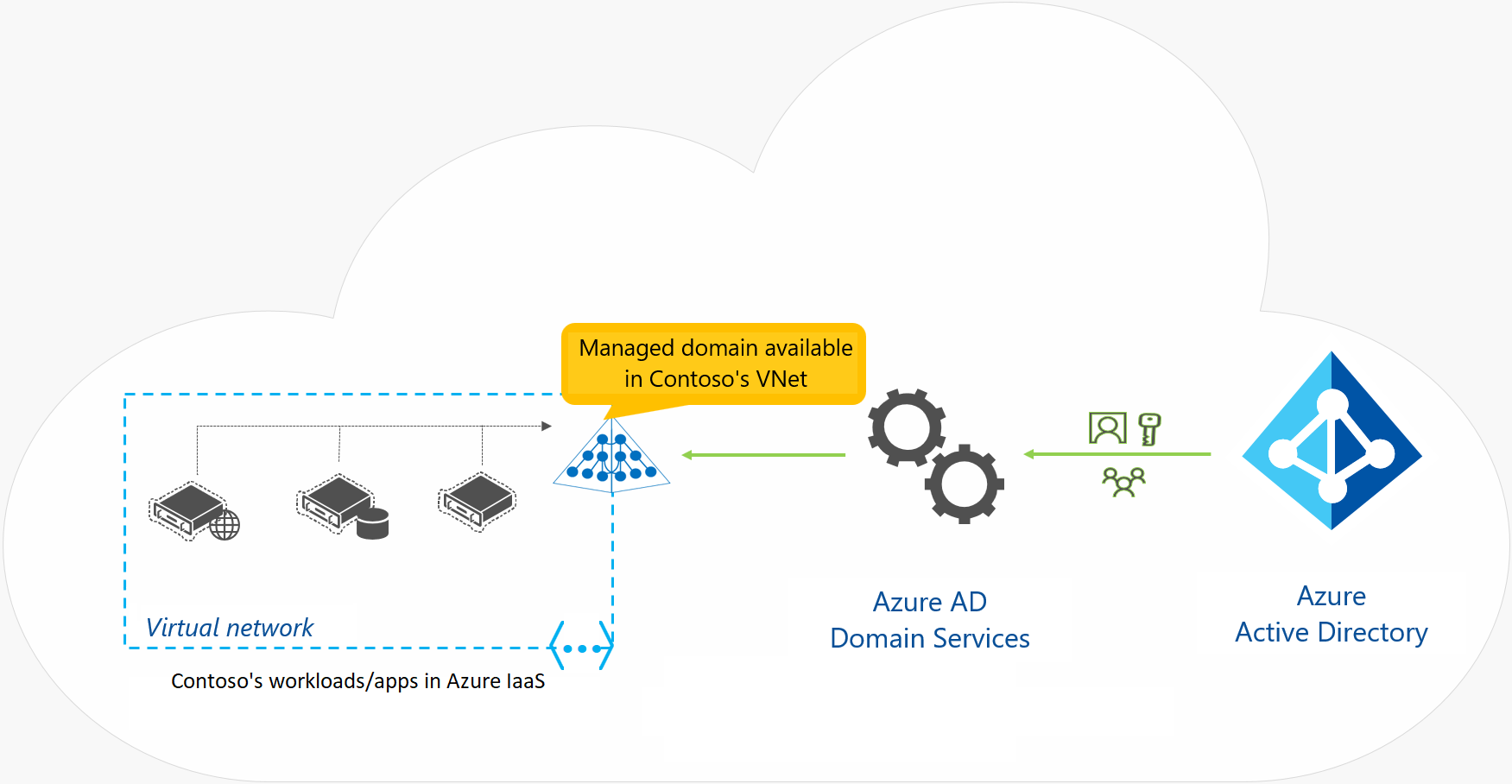
Compare Microsoft Entra ID and Active Directory Domain Services
Microsoft Entra ID and Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) share some common features but serve different purposes.
Characteristics of AD DS (Active Directory Domain Services)
- Traditional on-premises directory service.
- Based on X.500 hierarchy and DNS for resource location.
- Uses LDAP for queries and management.
- Authentication via Kerberos.
- Supports OUs (Organizational Units) and GPOs (Group Policy Objects) for management.
- Includes computer objects for domain-joined machines.
- Uses trusts between domains for delegation.
- Can be deployed on Azure VMs for scalability but does not integrate with Microsoft Entra ID natively.
Characteristics of Microsoft Entra ID
- Cloud-based identity solution designed for web applications.
- Multi-tenant directory service with a flat structure (no OUs or GPOs).
- Uses REST APIs over HTTP/HTTPS instead of LDAP.
- Authentication via SAML, WS-Federation, OpenID Connect (not Kerberos).
- Supports OAuth for authorization.
- Federation-ready, allowing integration with third-party identity providers like Facebook.
Key Differences
| Feature | AD DS | Microsoft Entra ID |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | On-premises | Cloud-based |
| Structure | Hierarchical (X.500, OUs) | Flat (no OUs, no GPOs) |
| Protocols | LDAP, Kerberos | REST API, SAML, OAuth |
| Authentication | Kerberos | OpenID, SAML, WS-Federation |
| Integration | Windows-based environments | Web and cloud apps |
| Federation | Requires AD FS | Built-in Federation |
Conclusion
While AD DS is designed for on-premises network management, Microsoft Entra ID is an internet-first identity provider for cloud applications. Many organizations use a hybrid approach, integrating Microsoft Entra ID with on-prem AD DS for seamless identity management. 🚀
Microsoft Entra ID as a Cloud Directory Service
Key Points:
- Cloud services like Microsoft 365, Azure, Dynamics 365, and Intune require a directory service for authentication and authorization.
- Instead of separate directories for each service, Microsoft Entra ID provides a single identity service for all Microsoft cloud services.
- It supports Single Sign-On (SSO) across Microsoft services and third-party platforms like Facebook, Google, and Yahoo.
- Developers can integrate Microsoft Entra ID authentication into custom applications using Azure portal and Microsoft Visual Studio.
- Azure App Service can be configured to restrict access to users from a designated Microsoft Entra tenant.
Conclusion
Microsoft Entra ID centralizes identity management for Microsoft and third-party cloud apps, simplifying authentication while enhancing security and access control. 🚀
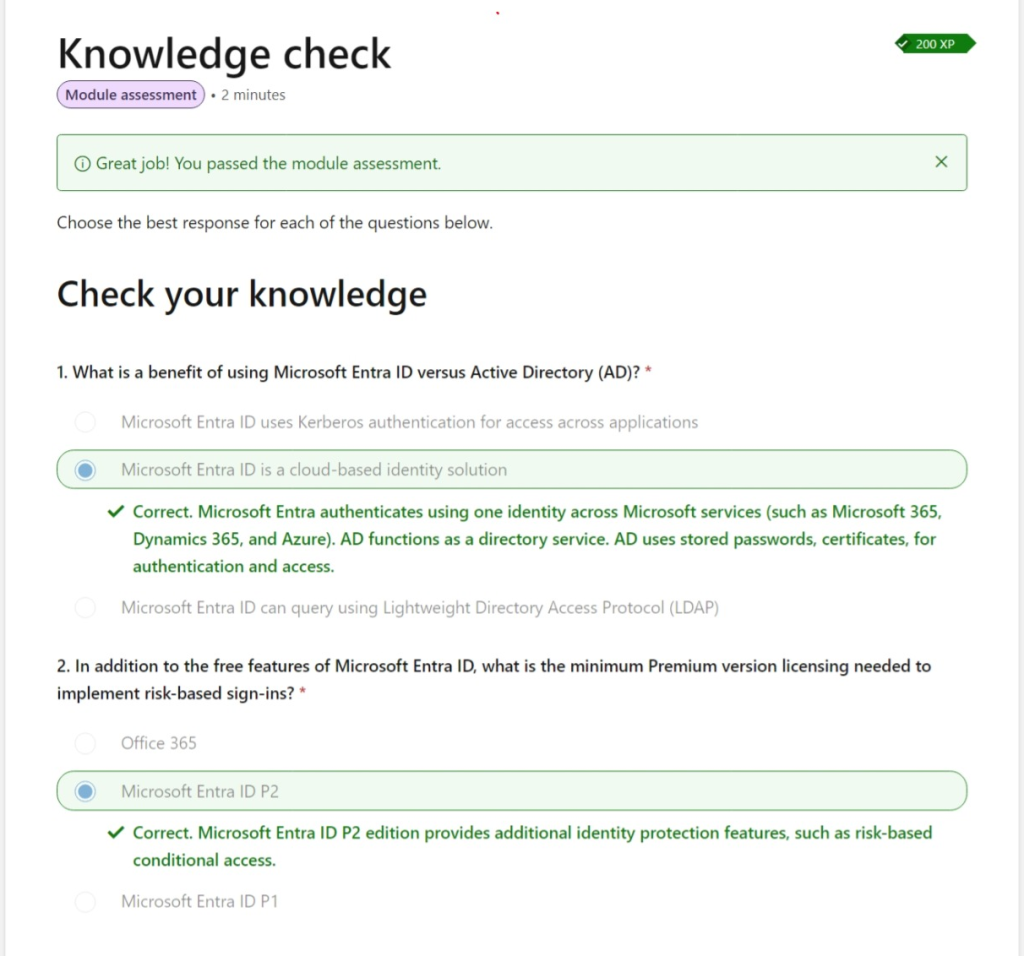
Comparison of Microsoft Entra ID P1 vs. P2 Plans
Common Features in P1 & P2 Plans
✅ Self-service group management – Users can create and manage groups, request to join, and approve memberships.
✅ Advanced security reports & alerts – Machine-learning-based reports detect anomalies and access risks.
✅ Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Works with on-prem apps (VPN, RADIUS), Azure, Microsoft 365, and third-party apps.
✅ Microsoft Identity Manager (MIM) licensing – Bridges on-prem authentication stores with Microsoft Entra ID.
✅ 99.9% SLA uptime guarantee – Ensures high availability.
✅ Password reset with writeback – Syncs with on-premises AD policies.
✅ Cloud App Discovery – Identifies frequently used cloud apps.
✅ Conditional Access – Controls access based on device, group, or location.
✅ Microsoft Entra Connect Health – Provides insights into operational performance and security.
Exclusive Features in P2 Plan
🔹 Microsoft Entra ID Protection – Monitors and protects accounts, allowing risk-based policies.
🔹 Privileged Identity Management (PIM) – Manages privileged roles, defines temporary admins, and enforces security workflows.
💡 Conclusion: P1 is suitable for standard security and access management, while P2 is ideal for advanced security and privileged access control. 🚀